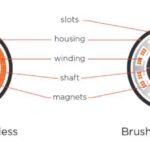
Brush Motor vs. Brushless Motor: Key Differences Explained
1. How a Brushed Motor Works
Brushed motors are among the most basic types of motors, often introduced in physics classes. They consist of three main components: the stator, rotor, and brushes. These motors generate motion through a rotating magnetic field, where the brushes and commutator maintain constant contact to conduct electricity and facilitate rotation.
Key Characteristics:
- Mechanical Commutation: The stator (magnets) remains stationary while the rotor (coils) rotates.
- Brush and Commutator System: Carbon brushes press against the commutator, delivering current to the coils. As the motor spins, the commutator switches the current direction to maintain motion.
- Friction and Wear: Continuous contact between brushes and commutator causes wear, requiring periodic brush replacement.
- Electrical Noise: Sparking between brushes and commutator can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI).
2. How a Brushless Motor Works
Brushless motors eliminate the need for physical brushes by using electronic commutation. Instead of brushes, they rely on sensors (such as Hall-effect sensors or magnetic encoders) and a controller to switch the current direction in the coils.
Key Characteristics:
- Electronic Commutation: The stator contains the coils, while the rotor holds permanent magnets.
- Precision Control: A motor controller adjusts power delivery for smooth operation, enabling advanced functions like speed adjustment, braking, and reverse rotation.
- No Brush Wear: Without brushes, there’s less friction, leading to longer lifespan and reduced maintenance.
- Higher Efficiency: Less energy is lost as heat, making brushless motors more efficient.

3. Speed Control Methods
Brushed Motors: Voltage Control
- Speed is adjusted by varying input voltage.
- Uses analog circuits (e.g., thyristors) for regulation.
- Simpler control mechanism but less precise.
Brushless Motors: Frequency Control
- Speed is adjusted by changing the switching frequency of MOSFETs in the controller.
- Uses digital control for more precise adjustments.
- Enables smoother acceleration and deceleration.
4. Performance Comparison
| Feature | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Lower (due to brush friction) | Higher (no brush losses) |
| Lifespan | Shorter (brush wear) | Longer (minimal wear) |
| Maintenance | Requires brush replacement | Virtually maintenance-free |
| Noise | Louder (brush friction & sparking) | Quieter (no brushes) |
| Control | Simpler, less precise | More precise, programmable |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Applications | Power tools, toys, basic appliances | Drones, EVs, HVAC systems, robotics |
5. Which One Should You Choose?
- Brushed Motors are cost-effective and suitable for simple, low-maintenance applications like household appliances and basic machinery.
- Brushless Motors excel in high-performance, long-life applications such as electric vehicles, drones, and industrial automation.
Final Verdict:
- Need affordability and simplicity? → Brushed motor
- Prioritize efficiency, durability, and precision? → Brushless motor
By understanding these differences, you can select the right motor for your needs while optimizing performance and longevity.
Electric motor supplier

Tattoo Machine Coreless Brush Motor BLDC Brushless Micro Mini Motor China Factory Manufacturer


We accept customized specification, contact us now for your requirement. We will be delighted to make samples for you.
Email: chinaok321@gmail.com Mob/Wechat/Whatsapp: 8613713792667 Skype: chinaok321